Paperjs:像素打印机
本文介绍一个像素打印机的小玩具
就是要在画布中,从左上角开始绘制指定大小的像素方块。从左到右,到了边缘折回继续。
思路:全局维护一个x,y,用来记录当前的位置,每帧的时候在该位置绘制方块,然后更新xy,直到到达画布的右下角。
效果如下: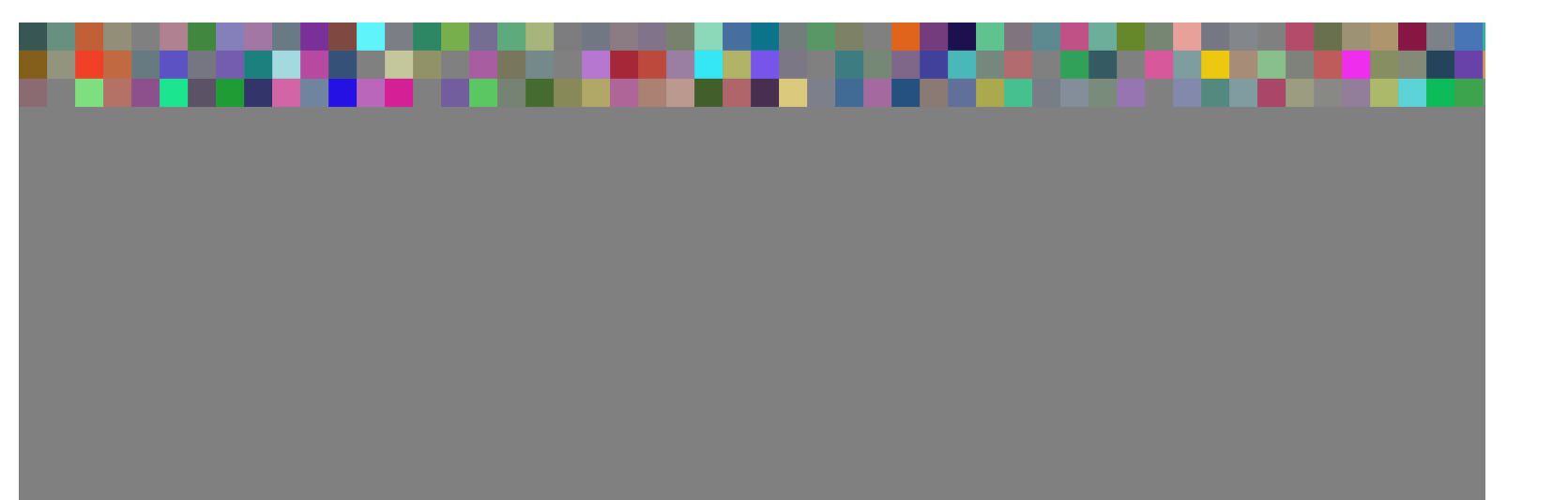
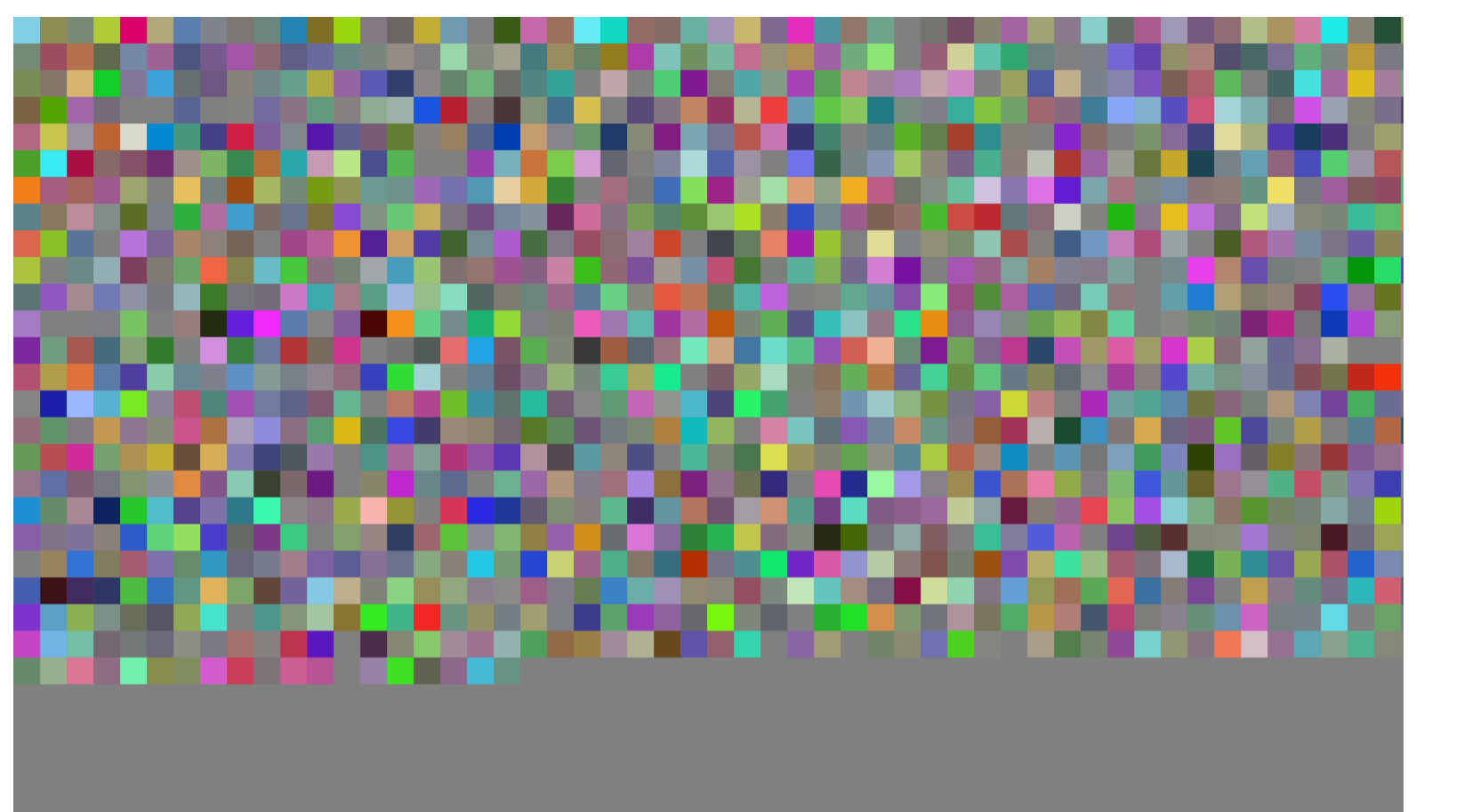
动图懒得搞了,将就着看吧。。。完整vue2代码:
<!--
* @Author: Hhvcg
* @Date: 2022-02-20 15:26:48
* @LastEditors: -_-
* @Description:
-->
<template>
<div class="dashboard">
<div class="dashboard-text flex-cc">
<span>
像素打印机
</span>
</div>
<div class="dashboard-container pd10 flex-cc">
<canvas id="main_canvas" ref="main_canvas" resize class="main_canvas" />
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
import paper from 'paper'
import {getRandomColor} from '../../weapons'
export default {
name: 'Dashboard',
computed: {
...mapGetters([
'name'
])
},
data() {
return {
paper: null,
tool: null,
// 存储画布容器宽高
XY: {},
SIZE: 20,
snake: {
x: null,
y: null,
direction: 1
}
}
},
created() {
},
mounted() {
this.initWorld()
// this.drawXY()
this.drawBrick()
},
methods: {
// 绘制snake的step
drawSnakeStep() {
if (this.snake.x >= this.XY.x || this.snake.y >= this.XY.y) return
// 根据当前snake的xy绘制图形
this.brick = new paper.Path.Rectangle(new paper.Point(this.snake.x, this.snake.y), new paper.Size(this.SIZE,this.SIZE))
this.brick.fillColor = getRandomColor()
if (Math.abs(this.snake.x + this.SIZE * this.snake.direction) <= this.XY.x) {
this.snake.x += this.SIZE * this.snake.direction
} else {
this.snake.y += this.SIZE
this.snake.direction = -this.snake.direction
}
},
onFrame() {
this.drawSnakeStep()
},
// 铺砖函数
drawBrick() {
},
// 绘制当前paperjs画布的坐标系
drawXY() {
this.X = new this.paper.Path()
this.X.strokeColor = 'black'
this.Y = new this.paper.Path()
this.Y.strokeColor = 'black'
for (let i = 0; i < this.XY.x / 2; i++) {
this.X.add(new paper.Point(i, 0))
this.X.add(new paper.Point(-i, 0))
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.XY.y / 2; i++) {
this.Y.add(new paper.Point(0, i))
this.Y.add(new paper.Point(0, -i))
}
},
initWorld() {
const canvas = this.$refs.main_canvas
this.XY.x = canvas.clientWidth
this.XY.y = canvas.clientHeight
this.snake.x = -Math.floor(canvas.clientWidth / 2)
this.snake.y = -Math.floor(canvas.clientHeight / 2)
console.log('xy', this.XY)
paper.setup(canvas)
this.paper = paper
this.paper.view.setCenter(0, 0);
this.paper.view.onFrame = this.onFrame
this.tool = new paper.Tool()
this.tool.onMouseDown = (e) => {
console.log('点击事件--->', e.point)
}
// 初始化世界
},
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.dashboard {
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 100%;
height: calc(100vh - 50px);
padding: 10px;
display: flex;
// justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
&-text {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid ghostwhite;
}
&-container {
height: calc(100% - 100px);
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid red;
.main_canvas {
width: 90%;
height: 90%;
background: gray;
}
}
}
</style>代码有些冗余,核心就是那个drawSnakeStep。
再来一幅有内涵的画: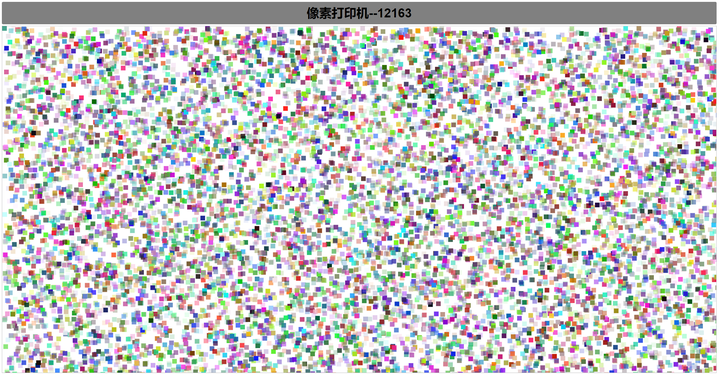
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
